6.vue不同的构建版本
leezozz 2/23/2023 vue
这里使用vuejs2.6.0版本
# 要点:
- 完整版:同时包含编译器和运行时版本
- 编译器:用来将模板字符串编译成为JavaScript渲染函数的代码,体积大、效率低(把模板转换成js渲染函数也就是render函数,render函数作用是生成虚拟DOM)(编译器约3000行左右)
- 运行时:用来创建vue实例、渲染并处理虚拟DOM等的代码,体积小、效率高。基本上就是除去编译器的代码
- UMD:UMD 版本通用的模块版本,支持多种模块方式(可以在浏览器直接使用)。 vue.js 默认文件就是运行时 + 编译器的UMD 版本
- CommonJS(cjs):CommonJS 版本用来配合老的打包工具比如 Browserify 或 webpack 1。
- ES Module:从 2.6 开始 Vue 会提供两个 ES Modules (ESM) 构建文件,为现代打包工具提供的版本。(ESM 格式被设计为可以被静态分析,所以打包工具可以利用这一点来进行“tree-shaking”并将用不到的代码排除出最终的包。)
- 推荐使用运行时版本,因为运行时版本相比完整版体积要小大约 30%
- 基于 Vue-CLI 创建的项目默认使用的是 vue.runtime.esm.js
导出 webpack 配置信息(导入到项目目录中),output.js 可修改成自定义文件名
// 使用vue-cli生成的项目默认使用esm版本vue,vue-cli对webpack进行了深度封装,在项目中找不到webpack的配置文件。使用如下命令可以查看
// 把配置文件输出到output文件中
vue inspect > output.js
// 下面是输出的配置文件
...
resolve: {
alias: {
'@': 'D:\\work\\03xxxxxxx',
vue$: 'vue/dist/vue.runtime.esm.js' // $:wepack的语法:精确匹配的意思
}
}
...
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
注意: .vue 文件中的模板是在构建时预编译的,最终打包后的结果不需要编译器,只需要运行时版本即可
# 问题:
观察下面代码,通过阅读源码,回答在页面上输出的结果
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
template: '<h3>Hello template</h3>',
render (h) {
return h('h4', 'Hello render')
}
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
注意:
- el不能是body、html标签
- 如果没有render,把template转换成render函数
- 如果有render方法,直接调用mount挂载DOM
// 1. el 不能是 body 或者 html
if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn( `Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead.` )
return this
}
const options = this.$options
if (!options.render) {
// 2. 把 template/el 转换成 render 函数
……
}
// 3. 调用 mount 方法,挂载 DOM
return mount.call(this, el, hydrating)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
结果: 页面渲染:Hello render
# 调试过程
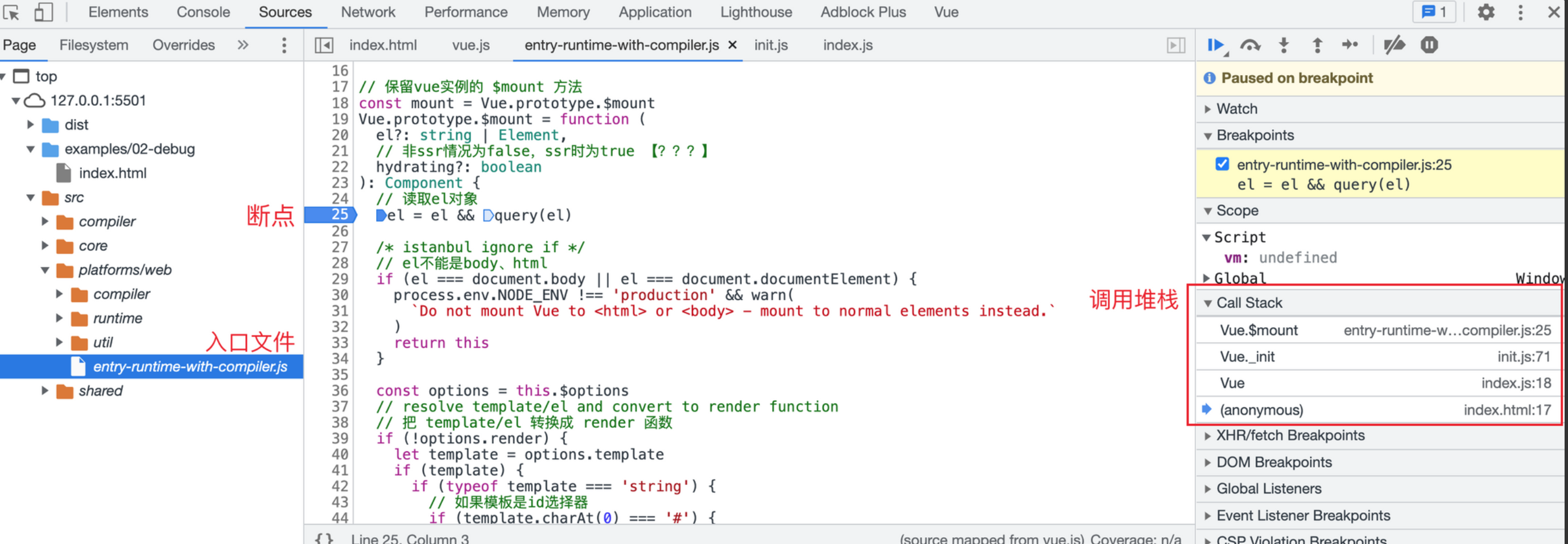 entry-runtime.png
entry-runtime.png
