20.js树广度、深度遍历
leezozz 3/11/2023 笔记
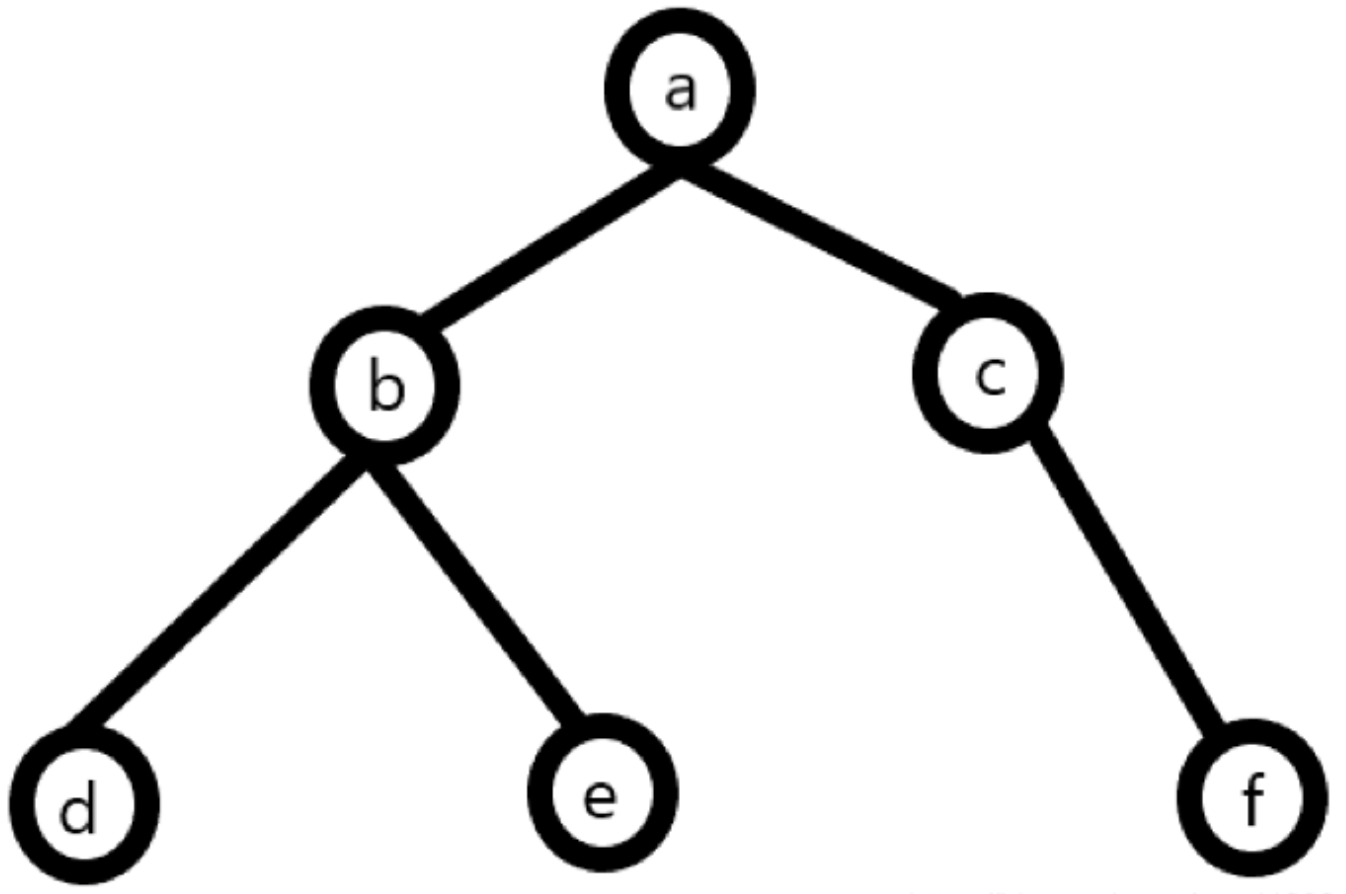
// 先定义一颗简单的树:
let tree = [
{
label:'a',
children:[
{
label:'b',
children:[
{
label:'d'
},
{
label:'e', // 没有children参数
}
]
},
{
label:'c',
children:[
{
label:'f',
children: [] // children参数为空数组【遍历时需要判断没有children,children参数为空数组这两种情况】
}
]
}
]
}
]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# 树的广度优先遍历
广度优先遍历:从上往下对每一层依次访问,对于上面这颗树的遍历顺序为abcdef(此处算法对应到二叉树上,属于先序遍历)
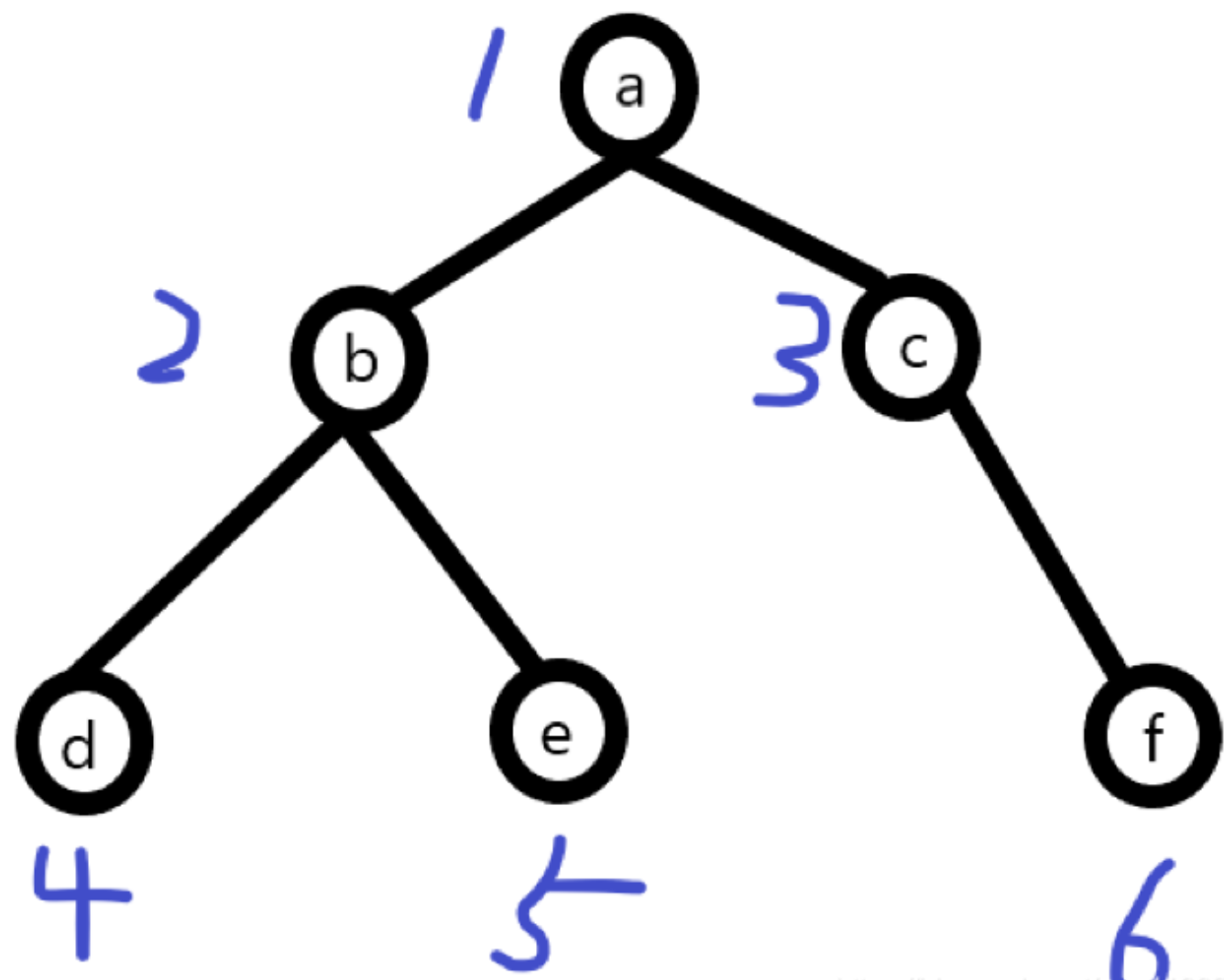
// 方法一:
let bf=function(tree){
let queue =tree;
const res = []
for(let i=0;i<queue.length;i++){
console.log(queue[i])
res.push(queue[i].label)
if(queue[i].children?.length) {queue=queue.concat(queue[i].children)}
}
return res
}
console.time('BFS-start')
const result =bf(tree);
console.log(JSON.stringify(result));
console.timeEnd('BFS-start')
// 方法二:
const deepBFS = (root, nodeList = []) => {
const queue = root;
// 循环判断队列的长度是否大于0
while(queue.length > 0) {
// 取出队列添加的节点
const p = queue.shift();
nodeList.push(p.label);
// 根据节点是否含有children,如果有子节点则添加到队列中
p.children?.length && p.children.forEach(v => queue.push(v))
}
return nodeList;
}
console.time('BFS-start')
const res = deepBFS(tree, []);
console.log(JSON.stringify(res));
console.timeEnd('BFS-start')
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# 树的深度遍历
深度遍历:对每一个可能的分支路径深入到不能再深入为止,对于上面这颗树的遍历顺序为abdecf
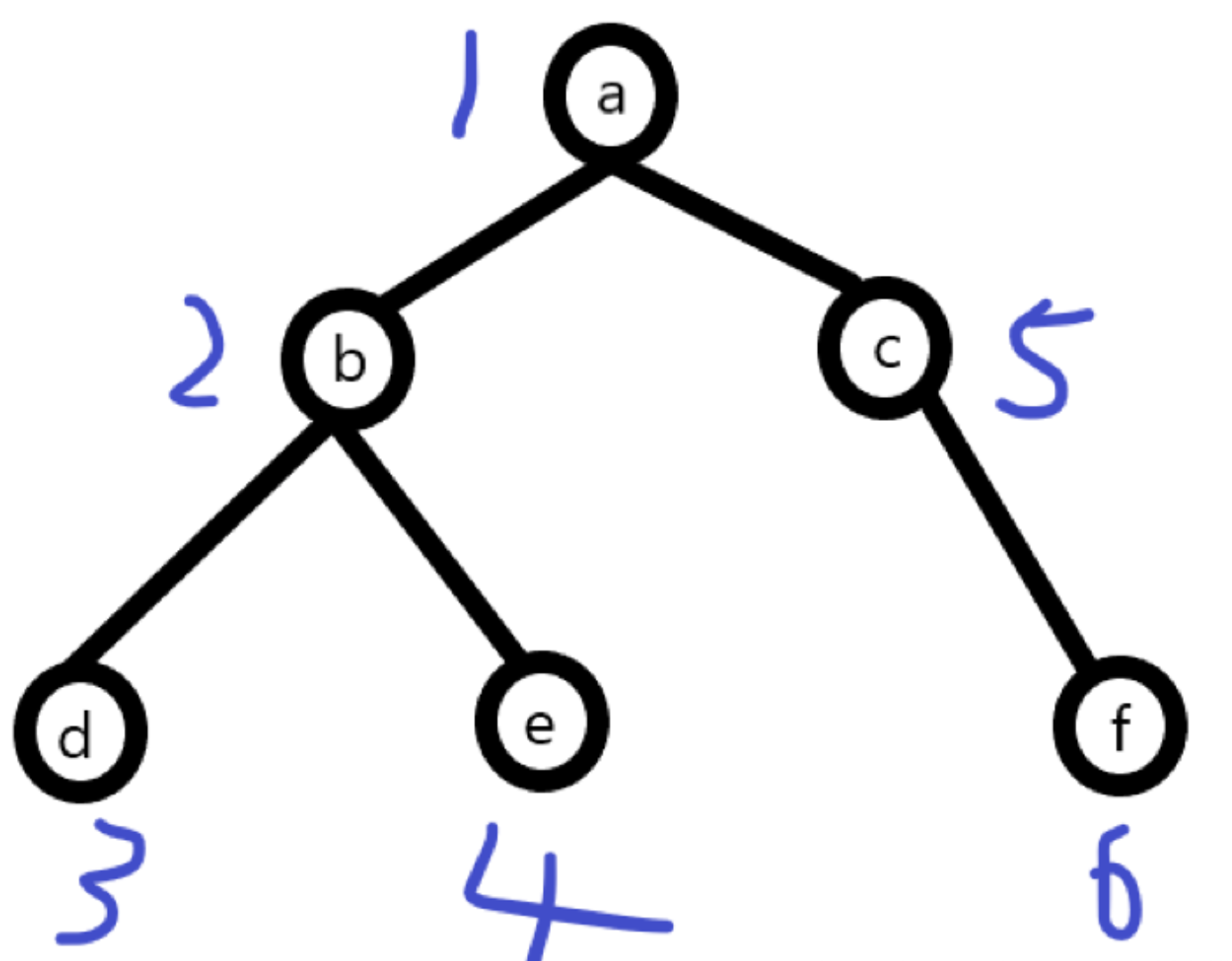
// 方法一:不使用递归
function dfsHandler(tree, callback) {
const treeBackup = [...tree];
const result = []
while(treeBackup.length) {
const _node = treeBackup.shift();
result.push(_node.label)
// 执行遍历回调方法
typeof callback === 'function' && callback(_node);
// 存在子节点时将子节点添加到待遍历数据的头部位置
_node.children && _node.children.length && treeBackup.unshift(..._node.children);
}
return result
}
dfsHandler(tree, (val) => {
console.log('val', val)
})
// 方法二:不使用递归(利用栈的特性)
// 1.创建一个栈(stack)用于保存待访问的节点
// 2.将根节点(node)压入栈中
// 3.进入循环,判断栈是否为空。如果栈不为空,则执行以下步骤:
// -弹出栈顶节点,将其赋值给变量_cur
// -访问当前节点的值,这里使用console.log进行输出,可以根据需要进行相应的处理
// -遍历当前节点的子节点(从右往左),将子节点逆序入栈
// 4.重复步骤3,直到栈为空
const depthFirstSearchIterative = (tree) => {
const stack = []
stack.push(tree)
let _cur = []
const res = []
while(stack.length) {
_cur = stack.pop()
res.push(_cur.label)
consle.log('_cur.label', _cur.label)
for(var i = _cur.children?.length-1; i >= 0; i--) {
// 判断children是否存在,children存在的话是否为空数组
if(_cur.children && _cur.children.length) {
stack.push(_cur.children[i])
}
}
}
return res
}
depthFirstSearchIterative(tree[0]) // ['a', 'b', 'd', 'e', 'c', 'f']
// 方法三:使用递归
const deepDFS = (root, nodeList = []) => {
if (root) {
nodeList.push(root.label);
// 递归root.children,找root的子节点
root.children && root.children.forEach(v => deepDFS(v, nodeList))
}
return nodeList;
}
const result = deepDFS(root[0], []);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
# 解答下面问题:
想定义一颗tree
const tree = {
id: 1,
children: [
{
id: 2,
children: [
{
id: 4,
children: []
},
{
id: 5,
children: [
{
id: 7,
children: []
}
]
}
]
},
{
id: 3,
children: [
{
id: 6,
children: [
{
id: 8,
children: []
}
]
}
]
}
]
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
# 1. 根据当前节点找到他的所有子节点
function findChildNodes(node, targetId) {
if (node.id === targetId) {
return node.children;
}
for (let i = 0; i < node.children.length; i++) {
const childNode = node.children[i];
const result = findChildNodes(childNode, targetId);
if (result) {
return result;
}
}
return null;
}
const currentNodeId = 2;
const childNodes = findChildNodes(tree, currentNodeId);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 2. 根据子节点向上查找他的所有父级节点
function findParentNodes(tree, targetId, parentNodes = []) {
if (tree.id === targetId) {
return parentNodes;
}
for (let i = 0; i < tree.children.length; i++) {
const childNode = tree.children[i];
const result = findParentNodes(childNode, targetId, [...parentNodes, tree]);
if (result) {
return result;
}
}
return null;
}
const currentNodeId = 7;
const parentNodes = findParentNodes(tree, currentNodeId);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 3. 根据当前子节点找到和他同级的所有节点
function findSiblingNodes(tree, targetId) {
const siblingNodes = [];
// 递归遍历树的函数
function traverse(node) {
if (!node || !node.children) {
return;
}
node.children.forEach(child => {
if (child.id === targetId) {
siblingNodes.push(...node.children.filter(sibling => sibling.id !== targetId));
return;
}
traverse(child);
});
}
traverse(tree);
return siblingNodes;
}
const currentNodeId = 5;
const siblingNodes = findSiblingNodes(tree, currentNodeId);
if (siblingNodes.length > 0) {
console.log("同级节点:", siblingNodes);
} else {
console.log("未找到指定节点或指定节点没有同级节点");
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32

Loading comments...